This article summarizes equations in the theory of electromagnetism.
DefinitionsEdit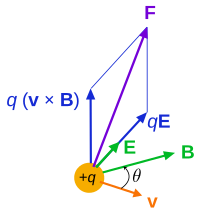
Lorentz force on a charged particle (of charge q) in motion (velocity v), used as the definition of the E field and B field.
Here subscripts e and m are used to differ between electric and magnetic charges. The definitions for monopoles are of theoretical interest, although real magnetic dipoles can be described using pole strengths. There are two possible units for monopole strength, Wb (Weber) and A m (Ampere metre). Dimensional analysis shows that magnetic charges relate by qm(Wb) = μ0 qm(Am).
Initial quantitiesEdit
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Electric charge | qe, q, Q | C = As | [I][T] |
|---|
| Monopole strength, magnetic charge | qm, g, p | Wb or Am | [L]2[M][T]−2 [I]−1 (Wb)
[I][L] (Am) |
|---|
Electric quantitiesEdit

Continuous charge distribution. The volume charge density ρ is the amount of charge per unit volume (cube), surface charge density σ is amount per unit surface area (circle) with outward unit normal n̂, d is the dipole moment between two point charges, the volume density of these is the polarization density P. Position vector r is a point to calculate the electric field; r′ is a point in the charged object.
Contrary to the strong analogy between (classical) gravitation and electrostatics, there are no "centre of charge" or "centre of electrostatic attraction" analogues.
Electric transport
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | Defining equation | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Linear, surface, volumetric charge density | λe for Linear, σe for surface, ρe for volume. |  

| C m−n, n = 1, 2, 3 | [I][T][L]−n |
|---|
| Capacitance | C |  V = voltage, not volume. | F = C V−1 | [I]2[T]4[L]−2[M]−1 |
|---|
| Electric current | I |  | A | [I] |
|---|
| Electric current density | J |  | A m−2 | [I][L]−2 |
|---|
| Displacement current density | Jd |  | A m−2 | [I][L]−2 |
|---|
| Convection current density | Jc |  | A m−2 | [I][L]−2 |
|---|
Electric fields
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | Defining equation | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Electric field, field strength, flux density, potential gradient | E |  | N C−1 = V m−1 | [M][L][T]−3[I]−1 |
|---|
| Electric flux | ΦE |  | N m2 C−1 | [M][L]3[T]−3[I]−1 |
|---|
| Absolute permittivity; | ε |  | F m−1 | [I]2 [T]4 [M]−1 [L]−3 |
|---|
| Electric dipole moment | p |  a = charge separation directed from -ve to +ve charge | C m | [I][T][L] |
|---|
| Electric Polarization, polarization density | P |  | C m−2 | [I][T][L]−2 |
|---|
| Electric displacement field | D |  | C m−2 | [I][T][L]−2 |
|---|
| Electric displacement flux | ΦD |  | C | [I][T] |
|---|
Absolute electric potential, EM scalar potential relative to point  Theoretical: 
Practical:  (Earth's radius) (Earth's radius)
| φ ,V |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| Voltage, Electric potential difference | Δφ,ΔV |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
Magnetic quantitiesEdit
Magnetic transport
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | Defining equation | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Linear, surface, volumetric pole density | λm for Linear, σm for surface, ρm for volume. |  

| Wb m−n
A m(−n + 1),
n = 1, 2, 3 | [L]2[M][T]−2 [I]−1 (Wb)
[I][L] (Am) |
|---|
| Monopole current | Im |  | Wb s−1
A m s−1 | [L]2[M][T]−3 [I]−1 (Wb)
[I][L][T]−1 (Am) |
|---|
| Monopole current density | Jm |  | Wb s−1 m−2
A m−1 s−1 | [M][T]−3 [I]−1 (Wb)
[I][L]−1[T]−1 (Am) |
|---|
Magnetic fields
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | Defining equation | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Magnetic field, field strength, flux density, induction field | B |  | T = N A−1 m−1 = Wb m−2 | [M][T]−2[I]−1 |
|---|
| Magnetic potential, EM vector potential | A |  | T m = N A−1 = Wb m3 | [M][L][T]−2[I]−1 |
|---|
| Magnetic flux | ΦB |  | Wb = T m2 | [L]2[M][T]−2[I]−1 |
|---|
| Magnetic permeability |  |  | V·s·A−1·m−1 = N·A−2 = T·m·A−1 = Wb·A−1·m−1 | [M][L][T]−2[I]−2 |
|---|
| Magnetic moment, magnetic dipole moment | m, μB, Π | Two definitions are possible: using pole strengths,
 using currents:
 a = pole separation N is the number of turns of conductor | A m2 | [I][L]2 |
|---|
| Magnetization | M |  | A m−1 | [I] [L]−1 |
|---|
| Magnetic field intensity, (AKA field strength) | H | Two definitions are possible: most common:
 using pole strengths,[1]
 | A m−1 | [I] [L]−1 |
|---|
| Intensity of magnetization, magnetic polarization | I, J |  | T = N A−1 m−1 = Wb m−2 | [M][T]−2[I]−1 |
|---|
| Self Inductance | L | Two equivalent definitions are possible: 

| H = Wb A−1 | [L]2 [M] [T]−2 [I]−2 |
|---|
| Mutual inductance | M | Again two equivalent definitions are possible: 

1,2 subscripts refer to two conductors/inductors mutually inducing voltage/ linking magnetic flux through each other. They can be interchanged for the required conductor/inductor; 

| H = Wb A−1 | [L]2 [M] [T]−2 [I]−2 |
|---|
| Gyromagnetic ratio (for charged particles in a magnetic field) | γ |  | Hz T−1 | [M]−1[T][I] |
|---|
Electric circuitsEdit
DC circuits, general definitions
Main article: Direct current
AC circuits
Main articles: Alternating current and Resonance
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | Defining equation | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Resistive load voltage | VR |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| Capacitive load voltage | VC |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| Inductive load voltage | VL |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| Capacitive reactance | XC |  | Ω−1 m−1 | [I]2 [T]3 [M]−2 [L]−2 |
|---|
| Inductive reactance | XL |  | Ω−1 m−1 | [I]2 [T]3 [M]−2 [L]−2 |
|---|
| AC electrical impedance | Z |  
| Ω−1 m−1 | [I]2 [T]3 [M]−2 [L]−2 |
|---|
| Phase constant | δ, φ |  | dimensionless | dimensionless |
|---|
| AC peak current | I0 |  | A | [I] |
|---|
| AC root mean square current | Irms | ![I_\mathrm{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{T} \int_{0}^{T} \left [ I \left ( t \right ) \right ]^2 \mathrm{d} t} \,\!](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a1def0a7f6e77cb4c21b955601a657047a645a97) | A | [I] |
|---|
| AC peak voltage | V0 |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| AC root mean square voltage | Vrms | ![V_\mathrm{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{T} \int_{0}^{T} \left [ V \left ( t \right ) \right ]^2 \mathrm{d} t} \,\!](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2a47cb2bc8518d427829d5d187367748f99a3dcf) | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| AC emf, root mean square |  |  | V = J C−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 [I]−1 |
|---|
| AC average power |  |  | W = J s−1 | [M] [L]2 [T]−3 |
|---|
| Capacitive time constant | τC |  | s | [T] |
|---|
| Inductive time constant | τL |  | s | [T] |
|---|
Magnetic circuitsEdit
Main article: Magnetic circuits
| Quantity (common name/s) | (Common) symbol/s | Defining equation | SI units | Dimension |
|---|
| Magnetomotive force, mmf | F,  |  N = number of turns of conductor | A | [I] |
|---|
ElectromagnetismEditElectric fieldsEdit
General Classical Equations
Magnetic fields and momentsEdit
See also: Magnetic moment
General classical equations
Electric circuits and electronicsEditBelow N = number of conductors or circuit components. Subcript net refers to the equivalent and resultant property value.
| Physical situation | Nomenclature | Series | Parallel |
|---|
| Resistors and conductors | - Ri = resistance of resistor or conductor i
- Gi = conductance of resistor or conductor i
|  
|  
|
|---|
| Charge, capacitors, currents | - Ci = capacitance of capacitor i
- qi = charge of charge carrier i
|   
|   
|
|---|
| Inductors | - Li = self-inductance of inductor i
- Lij = self-inductance element ij of L matrix
- Mij = mutual inductance between inductors i and j
|  |  
|
|---|
| Circuit | DC Circuit equations | AC Circuit equations |
|---|
Series circuit equations| RC circuits | Circuit equation 
Capacitor charge  Capacitor discharge  | |
|---|
| RL circuits | Circuit equation 
Inductor current rise  Inductor current fall  | |
|---|
| LC circuits | Circuit equation 
| Circuit equation 
Circuit resonant frequency  Circuit charge Circuit current Circuit electrical potential energy  Circuit magnetic potential energy  |
|---|
| RLC Circuits | Circuit equation 
| Circuit equation 
Circuit charge 
|
|---|

